Discover everything about Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), including symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment including diet, lifestyle changes, and medical options for hormonal balance, and how it affects fertility. Get expert insights to manage PCOS naturally and medically.
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal and metabolic disorder affecting women of reproductive age Characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excessive androgen (male hormone) levels, and polycystic ovaries(multiple small cysts on the ovaries),insulin resistance, and hormonal imbalances, increasing the risk of infertility. PCOS can impact a woman’s overall health,It is estimated that up to 1 in 10 women globally may have PCOS, many of whom remain undiagnosed.
PCOS is a leading cause of infertility, but it also increases the risk of:
Type 2 Diabetes (due to insulin resistance)
Cardiovascular Disease (linked to high cholesterol and blood pressure)
Endometrial Cancer (from prolonged absence of periods)
Mental Health Issues (anxiety, depression)

Symptoms of PCOS
The symptoms of PCOS vary from person to person but typically include:
Menstrual Irregularities
Oligomenorrhea (fewer than 8 periods per year)
Amenorrhea (no periods for 3+ months)
Heavy or prolonged bleeding when periods do occur
Hyperandrogenism (Excess Male Hormones)
Hirsutism: A condition in which excessive hair growth occurs on the face, chest, back, or thighs.
Acne (persistent, cystic, and often along the jawline)
Androgenic Alopecia (male-pattern hair thinning or baldness)
Metabolic & Weight-Related Issues
Insulin Resistance (leading to weight gain,fat deposition especially around the abdomen)
Difficulty losing weight despite diet and exercise
dark, velvety skin patches in body folds like the neck and armpits
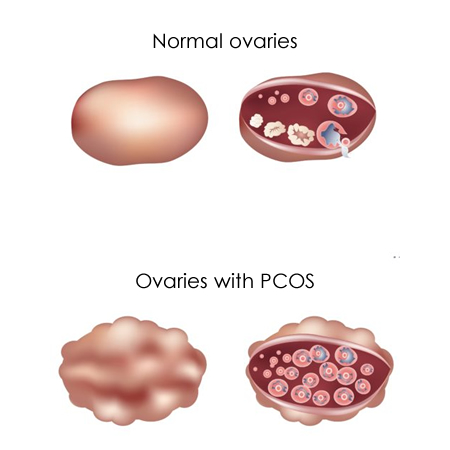
Polycystic Ovaries
Enlarged ovaries having multiple small cysts that are clearly visible on an ultrasound.
Fertility Challenges
Anovulation (lack of ovulation, making conception difficult)
Higher risk of miscarriage due to hormonal imbalances
Emotional & Psychological Effects
Mood swings, anxiety, and depression
Low self-esteem due to physical changes like weight gain and hair growth
Causes of PCOS
The actual cause of PCOS can not be known, but it is beleived that there are several factors which contribute such as
Insulin Resistance (Primary Driver)
A majority of women with PCOS have insulin resistance, leading to higher insulin levels,
High insulin levels stimulate the ovaries to produce more testosteron.
Leads to weight gain, difficulty losing fat, and increased diabetes risk.
Hormonal Imbalance
Elevated Luteinizing Hormone (LH) disrupts ovulation.
Low Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG) increases free testosterone.
High Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) suppresses follicle development.
Chronic Inflammation
Women with PCOS often have higher inflammatory markers (like CRP).Inflammation worsens insulin resistance and androgen production.
Genetic Predisposition
PCOS runs in families,if your mother or sister has it, your risk increases.Certain genes affect insulin signaling and steroid hormone production.
Environmental & Lifestyle Factors
Sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and stress contribute to hormonal imbalances.
How is PCOS Diagnosed?
There is no single test for diagnosing PCOS. Doctors use a combination of criteria and tests.The Criteria commonly used is, requiring at least two of the following symptoms
Hirsutism &Irregular or absent ovulation
Excess androgen levels. Clinical or biochemical signs of hyperandrogenism (high testosterone or symptoms like hirsutism)
Polycystic ovaries on ultrasound (12+ small follicles per ovary) and no ovulation.
Medical History
Including menstrual history, weight changes, and symptoms.
Blood Tests for PCOS
LH & FSH Ratio (LH is often 2-3x higher than FSH)
Testosterone & Free Androgen Index (FAI)
Fasting Insulin & Glucose (HOMA-IR test for insulin resistance)
AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone) Often elevated in PCOS
Thyroid & Prolactin (to rule out other conditions)
Treatment Options for PCOS
While there’s no cure for PCOS, several treatments help manage symptoms
Natural & Lifestyle Management
Best Diet for PCOS
Low Glycemic Index (GI) Foods:oats, quinoa, lentils, non-starchy veggies.
High-Fiber Foods:Flaxseeds, chia seeds, broccoli, and berries.
Healthy Fats : Avocados, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish (salmon).
Anti-inflammatory Spices :Turmeric, cinnamon, ginger.
Avoid: Sugar, refined carbs, processed foods, and trans fats.
Exercise for PCOS
Strength Training (3x/week),Improves insulin sensitivity.Regular physical activity helps regulate insulin levels and reduce weight. Regular physical activity helps regulate insulin levels and reduce weight.Even a 5-10% reduction in body weight can improve symptoms and fertility.
Stress & Sleep Management
Meditation & Deep Breathing – Lowers cortisol.
7-9 Hours of Sleep :Essential for hormonal balance.
Supplements for PCOS
Magnesium :Reduces insulin resistance.
Omega-3s:Lowers testosterone and inflammation.
Vitamin D: Many PCOS women are deficient.
Berberine: Natural alternative to Metformin.
Vitex (Chasteberry) :Helps regulate periods (but not for high androgens).
Alternative Therapies
Spearmint tea : Reduces excess hair growth.
Cinnamon : Helps regulate menstrual cycles.
Ashwagandha : Lowers cortisol and balances hormones.
Acupuncture : May improve ovulation and insulin sensitivity.
Medical Treatments for PCOS
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, doctors may recommend
Birth Control Pills
Birth Control Pills Regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels.Such as combined pills (estrogen + progestin) reduce androgens and regulate periods.Anti-androgenic pills (like Diane-35,spironolactone) help with acne and hirsutism.
Insulin-Sensitizing Drugs
Metformin improves insulin senstivity and may restore ovulation,regulates menstrual cycles, and helps with weight loss.
Inositol (Myo & D-Chiro) supplements work similarly to Metformin.
Surgical Options
A laparoscopic procedure to induce ovulation in women resistant to medications.
PCOS and Fertility
PCOS is the leading causes of female infertility because in PCOS there is irregular or absent ovulation. However, many women with PCOS can conceive with the right support:
Ovulation Induction: Using medications like clomiphene, letrozole, or gonadotropins.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): Such as In Vitro Fertilization (IVF).
Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss and diet can restore ovulation naturally in many cases.
It’s important for women with PCOS to work closely with a fertility specialist for personalized treatment plans.
Living with PCOS
Managing PCOS is a lifelong journey that involves a holistic approach to health
Regular monitoring of blood sugar and cholesterol is necessary to prevent diabestes and heart diseases.Mental health conditions like ,Anxiety and depression which are common in women with PCOS, can be managed by Therapy, support groups, and self-care.Endometrial Cancer can be prevented by Inducing periods (via birth control or progesterone).
Staying informed and seeking support from healthcare professionals and support groups is necessary.
Final Thoughts
PCOS is a complex condition, but with early diagnosis and tailored treatment, its symptoms and complications , including infertility, can be effectively managed. Whether through lifestyle adjustments, medical treatment, or fertility interventions, many women with PCOS go on to lead healthy lives and have children.
Consult an endocrinologist or nutritionist for a personalized PCOS treatment plan.